Abstract
Background: Isolated neutropenia is a common referral to pediatric hematology oncology. Guidelines exist regarding the management of severe congenital neutropenia as well as the differential diagnosis for isolated neutropenia. However, no expert guidelines exist to inform practice patterns on the diagnosis and management of patients with asymptomatic neutropenia or individuals with typical neutrophil counts associated with the Duffy null phenotype (Fy[a-/b-]). Understanding the practice patterns of pediatric hematologists oncologists may inform future efforts to reduce unnecessary medical testing and follow-up in these patient populations.
Methods: We distributed a twenty-one-question electronic survey to pediatric hematologists oncologists through the American Society of Pediatric Hematology Oncology's member discussion board from March 2022 until April 2022. The purpose of the survey was to identify practice patterns regarding patients referred for isolated neutropenia. Eligible participants included attending physicians and those who regularly see referrals for neutropenia. All trainees, advanced care providers, and individuals who do not regularly see patients with neutropenia were excluded. The survey explored: 1) common diagnostic studies physicians use to evaluate patients referred with asymptomatic and isolated neutropenia, 2) frequency of patient follow-up, 3) use of limited red cell phenotyping in pediatric patients with isolated neutropenia, 4) common terminology used to describe isolated neutropenia, and 5) whether physicians support removal of the term "benign ethnic neutropenia" from practice. We also presented two clinical case vignettes of asymptomatic and isolated neutropenia in a one-year-old male and a twelve-year old female. We compared management responses to the two vignettes to general neutropenia practice patterns.
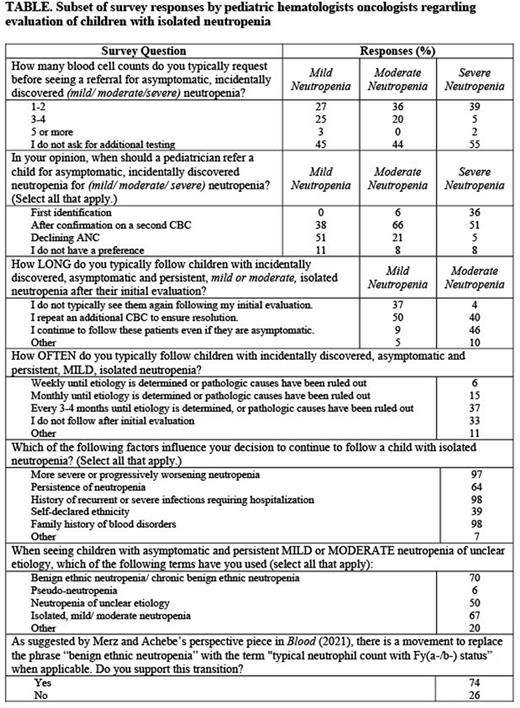
Results: One hundred and twenty-six pediatric hematology oncology attending physicians who regularly see neutropenia referrals completed the survey and were included in the analysis. Selected survey responses are shown in the Table. The most common tests ordered for pediatric patients with isolated neutropenia include complete blood cell count (CBC) (98%), peripheral smear (75%), anti-neutrophil antibody testing (29%), and immunoglobulins (24%). In the clinical vignettes, providers were more likely to order an anti-neutrophil antibody in toddlers (p=0.0085), and antinuclear antibody (ANA) panels in adolescents (p<0.001). Half of providers ask for additional CBCs prior to their initial consultation. Most respondents suggest referring patients with mild neutropenia after demonstrating a decline in absolute neutrophil count (ANC) (51%). For patients with mild neutropenia, most providers order an additional CBC to ensure resolution of their neutropenia or do not follow after their initial evaluation (87%). For patients with moderate neutropenia, most providers continue to follow patients even after their initial evaluation (46%). The three most important factors that influence continued follow-up of patients with isolated neutropenia include: history of recurrent/severe infections (98%), family history of blood disorders (98%), and more severe/progressively worsening neutropenia (97%). Seventy percent of respondents have diagnosed patients with the term "benign ethnic neutropenia," and 75% support replacement of the term to "typical neutrophil count with Fy(a-/b-) status," if confirmed with limited red cell phenotyping.
Conclusion: We identify the common practice patterns of pediatric hematologists oncologists caring for patients referred for asymptomatic and isolated neutropenia. Data from this study is providing the framework for a cost-effectiveness study aimed to reduce the healthcare and family burden of referrals for isolated neutropenia to pediatric hematologists oncologists. Furthermore, this survey demonstrates support for replacement of the term "benign ethnic neutropenia" with "typical neutrophil count with Fy(a-/b-) status" in applicable patients.
Disclosures
Powers:Pharmacosmos LLC: Consultancy; Women's Health Research Collaborative (WHrC)/ The Kinetix Group: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Lebensburger:Novartis: Consultancy; Forma Therapeutics: Consultancy; BPL: Consultancy; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal